It is the layered framework for the design of the network system that allows communication between all types of computer network.
It has seven separate layers and each layer call upon the services of the layer just below it.
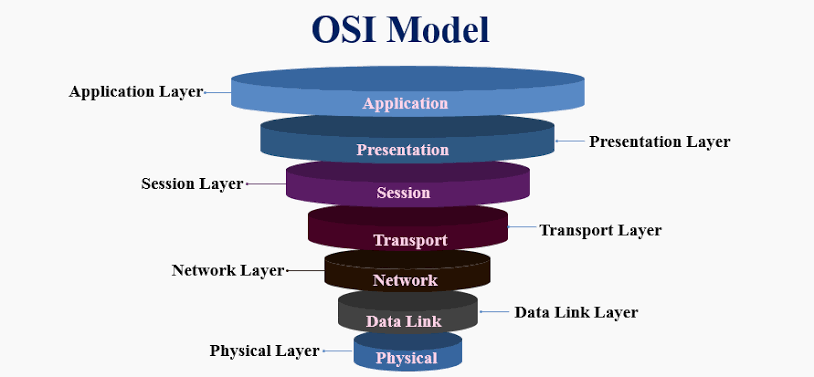
Layer 1 : Application layer
Layer 2 : Presentation layer
Layer 3 : Session layer
Layer 4 : Transport layer
Layer 5 : Network layer
Layer 6 : Datalink layer
Layer 7 : Physical layer
1. Physical layer – It is responsible for moving individual bit from one to next.
Functions
- It defines the type of transmission media.
- It defines the type of encoding to be used.
- It defines the duration of bit or the data rate. ( No. of bits send per second)
- Synchronisation of bits.
- Line configuration (point to point and multipoint)
- Topology
- Transmission mode ( simpler, half duplex, full duplex)
2. Datalink layer– It transforms physical link layer into reliable link.
Functions
- Framing i.e. conversion of bits to frame.
- Physical addressing i.e. describes header and footer.
- Access control used foe security purpose.
- Flow control i.e. the rate at which data should be send.
- Error control i.e. can be changed any bits.
3. Network layer– Responsible for source to duration delivery of packet.
Functions
- Header to packet coming from upper i.e. logical addressing.
- Which route needs to be choosed i.e. routing.
4. Transport layer– Responsible for process to process delivery.
Functions
- Service point addressing
- Segmentation and resemble
- Connection control i.e. connectionless and connection oriented.
- Flow and error control
5. Session layer– It is responsible for two functions that are dialogue control and synchronisation.
Functions
- Dialogue control- provides permission to control two systems and it could be either in half duplex and full duplex mode.
- Synchronisation is to add certain check points.
6. Presentation layer- It deals with the syntax and semantics of the information exchanged between two systems.
Functions
- Converting a message into compatible bit stream i.e. translation.
- Plain text into cioher text i.e. encryption.
- Reducing no. of bits contained in the information i.e. compression.
7. Application layer- It enables the user to access the network.
Functions
- Network virtual terminal i.e. software version of physical terminal.
- Email services and directory services.
- File transfer access and management.