In large networks, there can be multiple paths from sender to receiver. The switching technique will decide the best route for data transmission.
Switching technique is used to connect the systems for making one-to-one communication
There are basically three types of switching methods. Out of three methods, circuit switching and packet switching are commonly used but the message switching has been opposed out in the general communication procedure but is still used in the networking application.
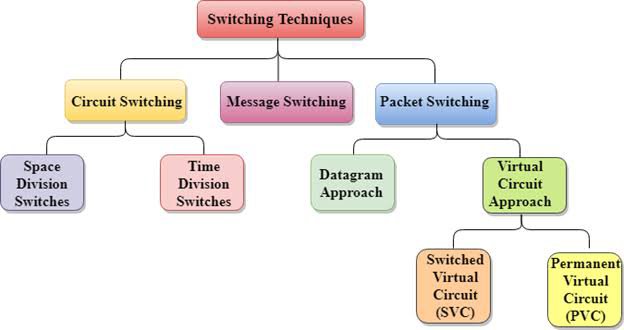
1. Circuit Switching
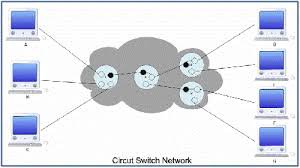
Circuit switching is a connection-oriented network switching technique. Here, a dedicated route is established between the source and the destination and the entire message is transferred through it.
It is of two types:
I. Space Division switch
A space division circuit switch is one in which all bits arriving on an input port are switched to a given output port. Crossbar switch. N inputs and N outputs; can connect any input to any output. Non-blocking: if the output line that you are trying to reach is free, the switch itself should not block the call.
II. Time Division switch
An all-electronic switching system based on time division multiplexing (TDM) principles: an input digitized signal from a source is connected to an output trunk by assigning a group of bits from the input data stream to a time slot in a high-speed TDM output data stream
Advantages
- It is suitable for long continuous transmission, since a continuous transmission route is established, that remains throughout the conversation.
- The dedicated path ensures a steady data rate of communication.
- No intermediate delays are found once the circuit is established. So, they are suitable for real time communication of both voice and data transmission.
Disadvantages
- Circuit switching establishes a dedicated connection between the end parties. This dedicated connection cannot be used for transmitting any other data, even if the data load is very low.
- Bandwidth requirement is high even in cases of low data volume.
- There is underutilization of system resources. Once resources are allocated to a particular connection, they cannot be used for other connections.
- Time required to establish connection may be high.
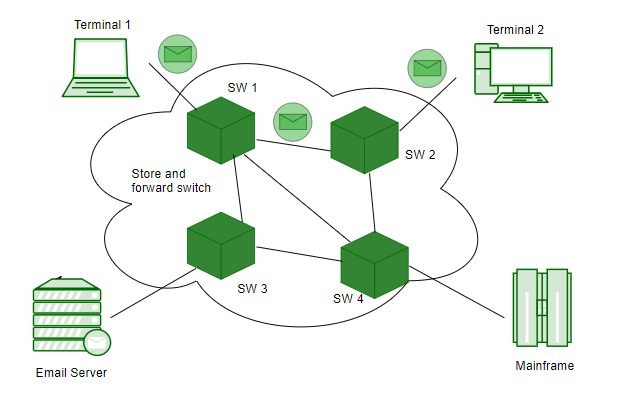
2. Message Switching
Message switching is a connectionless network switching technique where the entire message is routed from the source node to the destination node, one hop at a time. It was a precursor of packet switching.
Advantages
- As message switching is able to store the message for which communication channel is not available, it helps in reducing the traffic congestion in network.
- In message switching, the data channels are shared by the network devices.
- It makes the traffic management efficient by assigning priorities to the messages.
Disadvantages
- Message switching cannot be used for real time applications as storing of messages causes delay.
- In message switching, message has to be stored for which every intermediate devices in the network requires a large storing capacity.
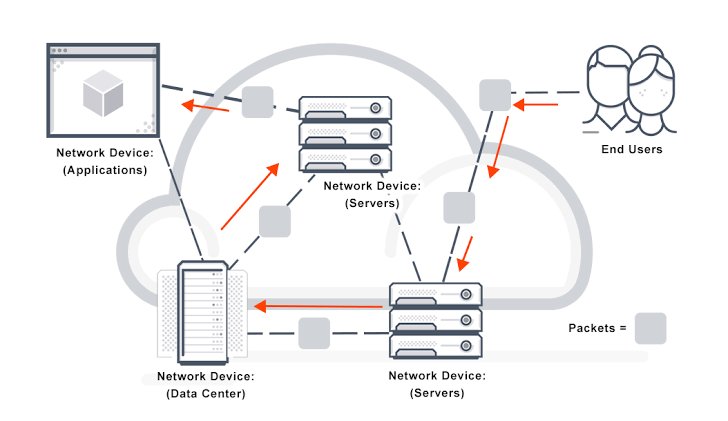
3. Packet Switching
Packet switching is a method of grouping data that is transmitted over a digital network into packets. Packets are made of a header and a payload. Data in the header is used by networking hardware to direct the packet to its destination where the payload is extracted and used by application software.
It is of two types:
I. Datagram Approach
Datagram packet-switching is a packet switching technology by which each packet, now called a datagram, is treated as a separate entity. Each packet is routed independently through the network. … The individual packets which form a data stream may follow different paths between the source and the destination.
II. Virtual Circuit Approach
A virtual circuit is a means of transporting data over a packet-switched network in such a way that it appears as though there is a dedicated physical link between the source and destination end systems of this data. The term virtual circuit is synonymous with virtual connection.
Advantages
- Delay in delivery of packets is less, since packets are sent as soon as they are available.
- Switching devices don’t require massive storage, since they don’t have to store the entire messages before forwarding them to the next node.
- Data delivery can continue even if some parts of the network faces link failure. Packets can be routed via other paths.
- It allows simultaneous usage of the same channel by multiple users.
- It ensures better bandwidth usage as a number of packets from multiple sources can be transferred via the same link.
Disadvantages
- They are unsuitable for applications that cannot afford delays in communication like high quality voice calls.
- Packet switching high installation costs.
- They require complex protocols for delivery.
- Network problems may introduce errors in packets, delay in delivery of packets or loss of packets. If not properly handled, this may lead to loss of critical information.