Network topology is schematic description of network arrangements, connecting various nodes (sender and receiver) through connecting lines.
There are following types of topologies:-
1. Star topology
2. Ring topology
3. Bus topology
4. Mesh topology
5. Tree topology
6. Hybrid topology
Further we will learn about them in detail:-
1. Mesh Topology
In mesh topology, every device is point to point connected to every other devices.
It creates a kind of mesh between each other.
Ex- In class every student is aware of his classmates and somehow connected to them to make it as a whole class. Similarly, in this also every device is interconnected to each other.
Advantages
1. Robust
2. Easily fault detection
3. Security
Disadvantages
1. Installation and configuration
2. Cost of maintenance
3. Cost of I/O port
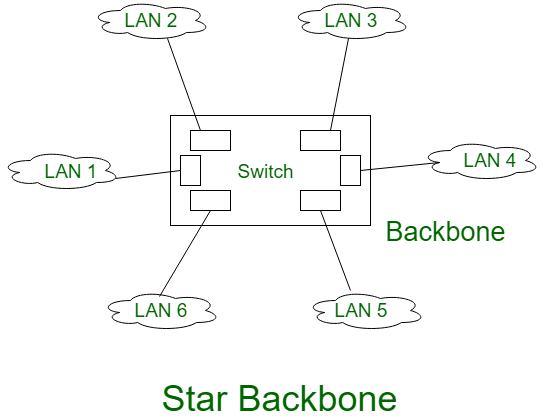
2. Star Topology
In star topology, each nodes has a dedicated point to point link to a Central controller i.e HUB.
The devices are not directly linked to each other.
To communication between two devices are done with the help of hub.
Star topology is much better than mesh topology because mesh topology is so complex whereas star topology is less complex.
Advantages
1. Robust
2. One link and one I/P port required
3. Easy installation and configuration
Disadvantages
1. Cost of installation and configuration is high
2. If hub fails, the whole system crashes
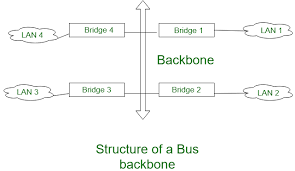
3. Bus topology
Bus topology is a multipoint structure.
One long cable act as a backbone to connect all nodes in the network.
The structure is constructed btw two points i.e start point and end point.
Advantages
1. Less cost of installation and configuration
2. One cable and n dropline are required
3. Cost is less then other topology
Disadvantages
1. If long cable is damaged then all the nodes connected to it will also stop working.
2. Collision of data is possible.
4. Ring Topology
By name it is clear that what is ring topology, In ring topology, the devices has dedicated point to point connection but only with two devices at a time.
There will be n no. of devices and n repeaters.
Advantages
1. Easy installation and configuration
2. Collision is minimum
Disadvantages
1. Addition or deletion of node disturbs whole topology.
2. Detection of trouble becomes difficult.
5. Tree Topology
The structure of tree topology is the same as we have learned it in data structure.
In tree topology, there exists one root node n the rest nodes are connected to it in the tree format.
It must be of atleast 3 level otherwise it won’t be considered as tree topology.
Advantages
1. Error detection is easy.
2. Nodes can be easily extended.
Disadvantages
1. Large amount of cable used.
2. Costly
6. Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology is a collection of two or more topologies i.e. star, bus and ring topologies.
The diagram of hybrid topology can created by joining the hubs of star, ring and bus topologies.
Advantages
1. Scalable coz size can be easily extended.
2. Flexible
Disadvantages
1. Design is complex